| Features > User Interface > Unsolicited User Interaction > Console Interaction |
The Console Interaction Provider uses standard console, available on most systems, for user input and output.
QuickOPC uses the Console Interaction Provider whenever the Environment.UserInteractive Property returns true, and the Windows Forms Interaction Provider does not take precedence. Note that it is also possible to use the Windows Forms Interaction in console applications, by referencing the Opclabs.QuickOpc.Forms package in the console-based project.
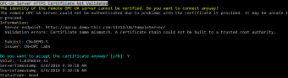
The example below triggers the component to ask the user whether he/she wants to accept the server's HTTPS certificate.
// This example shows how in a console application, the user is asked to accept a server HTTPS certificate. using System; using OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA; using OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.OperationModel; namespace UADocExamples.Interaction { partial class AcceptCertificate { public static void Https() { // Do not implicitly trust any endpoint URLs. We want the user be asked explicitly. EasyUAClient.SharedParameters.EngineParameters.CertificateAcceptancePolicy.TrustedEndpointUrlStrings.Clear(); // Define which server we will work with. UAEndpointDescriptor endpointDescriptor = "https://opcua.demo-this.com:51212/UA/SampleServer/"; // Instantiate the client object. var client = new EasyUAClient(); UAAttributeData attributeData; try { // Obtain attribute data. // The component automatically triggers the necessary user interaction during the first operation. attributeData = client.Read(endpointDescriptor, "nsu=http://test.org/UA/Data/ ;i=10853"); } catch (UAException uaException) { Console.WriteLine("*** Failure: {0}", uaException.GetBaseException().Message); return; } // Display results. Console.WriteLine("Value: {0}", attributeData.Value); Console.WriteLine("ServerTimestamp: {0}", attributeData.ServerTimestamp); Console.WriteLine("SourceTimestamp: {0}", attributeData.SourceTimestamp); Console.WriteLine("StatusCode: {0}", attributeData.StatusCode); } } }
# This example shows how in a console application, the user is asked to accept a server HTTPS certificate. # The QuickOPC package is needed. Install it using "pip install opclabs_quickopc". import opclabs_quickopc # Import .NET namespaces. from OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA import * from OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.OperationModel import * # Do not implicitly trust any endpoint URLs. We want the user be asked explicitly. EasyUAClient.SharedParameters.EngineParameters.CertificateAcceptancePolicy.TrustedEndpointUrlStrings.Clear() # Define which server we will work with. endpointDescriptor = UAEndpointDescriptor('https://opcua.demo-this.com:51212/UA/SampleServer/') # Instantiate the client object. client = EasyUAClient() try: # Obtain attribute data. # The component automatically triggers the necessary user interaction during the first operation. attributeData = IEasyUAClientExtension.Read(client, endpointDescriptor, UANodeDescriptor('nsu=http://test.org/UA/Data/ ;i=10853')) except UAException as uaException: print('*** Failure: ' + uaException.GetBaseException().Message) exit() # Display results. print('Value: ', attributeData.Value) print('ServerTimestamp: ', attributeData.ServerTimestamp) print('SourceTimestamp: ', attributeData.SourceTimestamp) print('StatusCode: ', attributeData.StatusCode) print() print('Finished.')
' This example shows how in a console application, the user is asked to accept a server HTTPS certificate. Imports OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA Imports OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.OperationModel Namespace Interaction Partial Friend Class AcceptCertificate Public Shared Sub Https() ' Do not implicitly trust any endpoint URLs. We want the user be asked explicitly. EasyUAClient.SharedParameters.EngineParameters.CertificateAcceptancePolicy.TrustedEndpointUrlStrings.Clear() ' Define which server we will work with. Dim endpointDescriptor As UAEndpointDescriptor = "https://opcua.demo-this.com:51212/UA/SampleServer/" ' Instantiate the client object. Dim client = New EasyUAClient() Dim attributeData As UAAttributeData Try ' Obtain attribute data. ' The component automatically triggers the necessary user interaction during the first operation. attributeData = client.Read(endpointDescriptor, "nsu=http://test.org/UA/Data/ ;i=10853") Catch uaException As UAException Console.WriteLine("*** Failure: {0}", uaException.GetBaseException.Message) Exit Sub End Try ' Display results. Console.WriteLine("Value: {0}", attributeData.Value) Console.WriteLine("ServerTimestamp: {0}", attributeData.ServerTimestamp) Console.WriteLine("SourceTimestamp: {0}", attributeData.SourceTimestamp) Console.WriteLine("StatusCode: {0}", attributeData.StatusCode) End Sub End Class End Namespace
// This example shows how in a console application, the user is asked to accept a server HTTPS certificate. class procedure AcceptCertificate.Https; var AttributeData: _UAAttributeData; Client: OpcLabs_EasyOpcUA_TLB._EasyUAClient; ClientManagement: TEasyUAClientManagement; EndpointDescriptor: string; begin // The configuration object allows access to static behavior. ClientManagement := TEasyUAClientManagement.Create(nil); ClientManagement.Connect; // Do not implicitly trust any endpoint URLs. We want the user be asked explicitly. ClientManagement.SharedParameters.EngineParameters.CertificateAcceptancePolicy.TrustedEndpointUrlStrings.Clear(); // Define which server we will work with. EndpointDescriptor := 'https://opcua.demo-this.com:51212/UA/SampleServer/'; // Instantiate the client object. Client := CoEasyUAClient.Create; try // Obtain attribute data. // The component automatically triggers the necessary user interaction during the first operation. AttributeData := Client.Read(EndpointDescriptor, 'nsu=http://test.org/UA/Data/ ;i=10853'); except on E: EOleException do begin WriteLn(Format('*** Failure: %s', [E.GetBaseException.Message])); Exit; end; end; // Display results. WriteLn('Value: ', AttributeData.Value); WriteLn('ServerTimestamp: ', DateTimeToStr(AttributeData.ServerTimestamp)); WriteLn('SourceTimestamp: ', DateTimeToStr(AttributeData.SourceTimestamp)); WriteLn('StatusCode: ', AttributeData.StatusCode.ToString); FreeAndNil(ClientManagement); end;
The program output may look like this:
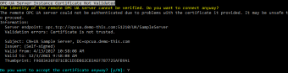
The example below triggers the component to ask the user whether he/she wants to accept the server's instance certificate.
// This example shows how in a console application, the user is asked to accept a server instance certificate. using System; using OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA; using OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.Engine; using OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.OperationModel; namespace UADocExamples.Interaction { partial class AcceptCertificate { public static void Instance() { // Do not implicitly trust any endpoint URLs. We want the user be asked explicitly. EasyUAClient.SharedParameters.EngineParameters.CertificateAcceptancePolicy.TrustedEndpointUrlStrings.Clear(); // Define which server we will work with. UAEndpointDescriptor endpointDescriptor = "opc.tcp://opcua.demo-this.com:51210/UA/SampleServer"; // Require secure connection, in order to enforce the certificate check. endpointDescriptor.EndpointSelectionPolicy = UAMessageSecurityModes.Secure; // Instantiate the client object. var client = new EasyUAClient(); UAAttributeData attributeData; try { // Obtain attribute data. // The component automatically triggers the necessary user interaction during the first operation. attributeData = client.Read(endpointDescriptor, "nsu=http://test.org/UA/Data/ ;i=10853"); } catch (UAException uaException) { Console.WriteLine("*** Failure: {0}", uaException.GetBaseException().Message); return; } // Display results. Console.WriteLine("Value: {0}", attributeData.Value); Console.WriteLine("ServerTimestamp: {0}", attributeData.ServerTimestamp); Console.WriteLine("SourceTimestamp: {0}", attributeData.SourceTimestamp); Console.WriteLine("StatusCode: {0}", attributeData.StatusCode); } } }
# This example shows how in a console application, the user is asked to accept a server instance certificate. # The QuickOPC package is needed. Install it using "pip install opclabs_quickopc". import opclabs_quickopc # Import .NET namespaces. from OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA import * from OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.Engine import * from OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.OperationModel import * # Do not implicitly trust any endpoint URLs. We want the user be asked explicitly. EasyUAClient.SharedParameters.EngineParameters.CertificateAcceptancePolicy.TrustedEndpointUrlStrings.Clear() # Define which server we will work with. endpointDescriptor = UAEndpointDescriptor('opc.tcp://opcua.demo-this.com:51210/UA/SampleServer') # Require secure connection, in order to enforce the certificate check. endpointDescriptor.EndpointSelectionPolicy = UAEndpointSelectionPolicy(UAMessageSecurityModes.Secure) # Instantiate the client object. client = EasyUAClient() try: # Obtain attribute data. # The component automatically triggers the necessary user interaction during the first operation. attributeData = IEasyUAClientExtension.Read(client, endpointDescriptor, UANodeDescriptor('nsu=http://test.org/UA/Data/ ;i=10853')) except UAException as uaException: print('*** Failure: ' + uaException.GetBaseException().Message) exit() # Display results. print('Value: ', attributeData.Value) print('ServerTimestamp: ', attributeData.ServerTimestamp) print('SourceTimestamp: ', attributeData.SourceTimestamp) print('StatusCode: ', attributeData.StatusCode) print() print('Finished.')
' This example shows how in a console application, the user is asked to accept a server instance certificate. Imports OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA Imports OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.Engine Imports OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.OperationModel Namespace Interaction Partial Friend Class AcceptCertificate Public Shared Sub Instance() ' Do not implicitly trust any endpoint URLs. We want the user be asked explicitly. EasyUAClient.SharedParameters.EngineParameters.CertificateAcceptancePolicy.TrustedEndpointUrlStrings.Clear() ' Define which server we will work with. Dim endpointDescriptor As UAEndpointDescriptor = "opc.tcp://opcua.demo-this.com:51210/UA/SampleServer" ' Require secure connection, in order to enforce the certificate check. endpointDescriptor.EndpointSelectionPolicy = UAMessageSecurityModes.Secure ' Instantiate the client object. Dim client = New EasyUAClient() Dim attributeData As UAAttributeData Try ' Obtain attribute data. ' The component automatically triggers the necessary user interaction during the first operation. attributeData = client.Read(endpointDescriptor, "nsu=http://test.org/UA/Data/ ;i=10853") Catch uaException As UAException Console.WriteLine("*** Failure: {0}", uaException.GetBaseException.Message) Exit Sub End Try ' Display results. Console.WriteLine("Value: {0}", attributeData.Value) Console.WriteLine("ServerTimestamp: {0}", attributeData.ServerTimestamp) Console.WriteLine("SourceTimestamp: {0}", attributeData.SourceTimestamp) Console.WriteLine("StatusCode: {0}", attributeData.StatusCode) End Sub End Class End Namespace
// This example shows how in a console application, the user is asked to accept a server instance certificate. class procedure AcceptCertificate.Instance; var Arguments: OleVariant; AttributeData: _UAAttributeData; Client: OpcLabs_EasyOpcUA_TLB._EasyUAClient; ClientManagement: TEasyUAClientManagement; EndpointSelectionPolicy: _UAEndpointSelectionPolicy; ReadArguments: _UAReadArguments; Result: _UAAttributeDataResult; Results: OleVariant; begin // The configuration object allows access to static behavior. ClientManagement := TEasyUAClientManagement.Create(nil); ClientManagement.Connect; // Do not implicitly trust any endpoint URLs. We want the user be asked explicitly. ClientManagement.SharedParameters.EngineParameters.CertificateAcceptancePolicy.TrustedEndpointUrlStrings.Clear(); // Define which server we will work with. ReadArguments := CoUAReadArguments.Create; ReadArguments.EndpointDescriptor.UrlString := 'opc.tcp://opcua.demo-this.com:51210/UA/SampleServer'; // Require secure connection, in order to enforce the certificate check. EndpointSelectionPolicy := CoUAEndpointSelectionPolicy.Create; EndpointSelectionPolicy.AllowedMessageSecurityModes := UAMessageSecurityModes_Secure; ReadArguments.EndpointDescriptor.EndpointSelectionPolicy := EndpointSelectionPolicy; ReadArguments.NodeDescriptor.NodeId.ExpandedText := 'nsu=http://test.org/UA/Data/ ;i=10853'; Arguments := VarArrayCreate([0, 0], varVariant); Arguments[0] := ReadArguments; // Instantiate the client object. Client := CoEasyUAClient.Create; // Obtain attribute data. // The component automatically triggers the necessary user interaction during the first operation. TVarData(Results).VType := varArray or varVariant; TVarData(Results).VArray := PVarArray(Client.ReadMultiple(Arguments)); Result := IInterface(Results[0]) as _UAAttributeDataResult; if Result.Succeeded then begin AttributeData := Result.AttributeData; // Display results. WriteLn('Value: ', AttributeData.Value); WriteLn('ServerTimestamp: ', DateTimeToStr(AttributeData.ServerTimestamp)); WriteLn('SourceTimestamp: ', DateTimeToStr(AttributeData.SourceTimestamp)); WriteLn('StatusCode: ', AttributeData.StatusCode.ToString); end else WriteLn('*** Failure: ', Result.ErrorMessageBrief); VarClear(Results); VarClear(Arguments); FreeAndNil(ClientManagement); end;
The program output may look like this:
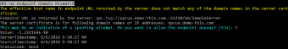
The example below triggers the component to ask the user whether he/she wants to accept an instance certificate whose domain does not match the URL used to connect to the server.
// This example shows how in a console application, the user is asked to allow a server instance certificate with // mismatched domain name. using System; using OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA; using OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.OperationModel; namespace UADocExamples.Interaction { class AllowEndpointDomain { public static void Main1() { // Define which server we will work with. // Note that extra '.' at the end of the domain name. For the purpose of this example, it allows us to address // the same domain, but cause a mismatch with what the names that are listed in the server instance certificate. UAEndpointDescriptor endpointDescriptor = "opc.tcp://opcua.demo-this.com.:51210/UA/SampleServer"; // Instantiate the client object. var client = new EasyUAClient() { // Enforce the endpoint domain check. Isolated = true, IsolatedParameters = {SessionParameters = {CheckEndpointDomain = true}} }; UAAttributeData attributeData; try { // Obtain attribute data. // The component automatically triggers the necessary user interaction during the first operation. attributeData = client.Read(endpointDescriptor, "nsu=http://test.org/UA/Data/ ;i=10853"); } catch (UAException uaException) { Console.WriteLine("*** Failure: {0}", uaException.GetBaseException().Message); return; } // Display results. Console.WriteLine("Value: {0}", attributeData.Value); Console.WriteLine("ServerTimestamp: {0}", attributeData.ServerTimestamp); Console.WriteLine("SourceTimestamp: {0}", attributeData.SourceTimestamp); Console.WriteLine("StatusCode: {0}", attributeData.StatusCode); } } }
# This example shows how in a console application, the user is asked to allow a server instance certificate with # mismatched domain name. # The QuickOPC package is needed. Install it using "pip install opclabs_quickopc". import opclabs_quickopc # Import .NET namespaces. from OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA import * from OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.OperationModel import * # Define which server we will work with. # Note that extra '.' at the end of the domain name. For the purpose of this example, it allows us to address # the same domain, but cause a mismatch with what the names that are listed in the server instance certificate. endpointDescriptor = UAEndpointDescriptor('opc.tcp://opcua.demo-this.com.:51210/UA/SampleServer') # Instantiate the client object. client = EasyUAClient() # Enforce the endpoint domain check. client.Isolated = True client.IsolatedParameters.SessionParameters.CheckEndpointDomain = True try: # Obtain attribute data. # The component automatically triggers the necessary user interaction during the first operation. attributeData = IEasyUAClientExtension.Read(client, endpointDescriptor, UANodeDescriptor('nsu=http://test.org/UA/Data/ ;i=10853')) except UAException as uaException: print('*** Failure: ' + uaException.GetBaseException().Message) exit() # Display results. print('Value: ', attributeData.Value) print('ServerTimestamp: ', attributeData.ServerTimestamp) print('SourceTimestamp: ', attributeData.SourceTimestamp) print('StatusCode: ', attributeData.StatusCode) print() print('Finished.')
' This example shows how in a console application, the user is asked to allow a server instance certificate with ' mismatched domain name. Imports OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA Imports OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.OperationModel Imports OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.Engine Namespace Interaction Friend Class AllowEndpointDomain Public Shared Sub Main1() ' Define which server we will work with. ' Note that extra '.' at the end of the domain name. For the purpose of this example, it allows us to address ' the same domain, but cause a mismatch with what the names that are listed in the server instance certificate. Dim endpointDescriptor As UAEndpointDescriptor = "opc.tcp://opcua.demo-this.com.:51210/UA/SampleServer" ' Instantiate the client object. Dim client = New EasyUAClient() With _ { _ .Isolated = True, _ .IsolatedParameters = New EasyUAAdaptableParameters() With _ { _ .SessionParameters = New UASmartSessionParameters() With _ { _ .CheckEndpointDomain = True _ } _ } _ } Dim attributeData As UAAttributeData Try ' Obtain attribute data. ' The component automatically triggers the necessary user interaction during the first operation. attributeData = client.Read(endpointDescriptor, "nsu=http://test.org/UA/Data/ ;i=10853") Catch uaException As UAException Console.WriteLine("*** Failure: {0}", uaException.GetBaseException.Message) Exit Sub End Try ' Display results. Console.WriteLine("Value: {0}", attributeData.Value) Console.WriteLine("ServerTimestamp: {0}", attributeData.ServerTimestamp) Console.WriteLine("SourceTimestamp: {0}", attributeData.SourceTimestamp) Console.WriteLine("StatusCode: {0}", attributeData.StatusCode) End Sub End Class End Namespace
// This example shows how in a console application, the user is asked to allow a server instance certificate with // mismatched domain name. class procedure AllowEndpointDomain.Main; var AttributeData: _UAAttributeData; Client: _EasyUAClient; EndpointDescriptor: string; begin // Define which server we will work with. // Note that extra '.' at the end of the domain name. For the purpose of this example, it allows us to address // the same domain, but cause a mismatch with what the names that are listed in the server instance certificate. EndpointDescriptor := 'opc.tcp://opcua.demo-this.com.:51210/UA/SampleServer'; // Instantiate the client object. Client := CoEasyUAClient.Create; // Enforce the endpoint domain check. Client.Isolated := true; Client.IsolatedParameters.SessionParameters.CheckEndpointDomain := true; try // Obtain attribute data. // The component automatically triggers the necessary user interaction during the first operation. AttributeData := Client.Read(EndpointDescriptor, 'nsu=http://test.org/UA/Data/ ;i=10853'); except on E: EOleException do begin WriteLn(Format('*** Failure: %s', [E.GetBaseException.Message])); Exit; end; end; // Display results. WriteLn('Value: ', AttributeData.Value); WriteLn('ServerTimestamp: ', DateTimeToStr(AttributeData.ServerTimestamp)); WriteLn('SourceTimestamp: ', DateTimeToStr(AttributeData.SourceTimestamp)); WriteLn('StatusCode: ', AttributeData.StatusCode.ToString); end;
Rem This example shows how in a console application, the user is asked to allow a server instance certificate with Rem mismatched domain name. Option Explicit ' Define which server we will work with. ' Note that extra '.' at the end of the domain name. For the purpose of this example, it allows us to address ' the same domain, but cause a mismatch with what the names that are listed in the server instance certificate. Dim endpointDescriptor: endpointDescriptor = "opc.tcp://opcua.demo-this.com.:51210/UA/SampleServer" ' Instantiate the client object. Dim Client: Set Client = CreateObject("OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.EasyUAClient") ' Enforce the endpoint domain check. Client.Isolated = True Client.IsolatedParameters.SessionParameters.CheckEndpointDomain = True ' Obtain attribute data. ' The component automatically triggers the necessary user interaction during the first operation. On Error Resume Next Dim AttributeData: Set AttributeData = Client.Read(endpointDescriptor, "nsu=http://test.org/UA/Data/ ;i=10853") If Err.Number <> 0 Then WScript.Echo "*** Failure: " & Err.Source & ": " & Err.Description WScript.Quit End If On Error Goto 0 ' Display results WScript.Echo "Value: " & AttributeData.Value WScript.Echo "ServerTimestamp: " & AttributeData.ServerTimestamp WScript.Echo "SourceTimestamp: " & AttributeData.SourceTimestamp WScript.Echo "StatusCode: " & AttributeData.StatusCode ' Example output: ' 'OPC-UA Endpoint Domain Mismatch 'The effective host name in endpoint URL returned by the server does not match any of the domain names in the server certificate. 'Endpoint URL as returned by the server: opc.tcp://opcua.demo-this.com.:51210/UA/SampleServer 'The server certificate is for following domain names or IP addresses: opcua.demo-this.com 'This may be an indication of a spoofing attempt. Do you want to allow the endpoint anyway? [Y/n]: Y 'Value: -1.285897E+14 'ServerTimestamp: 11/28/2019 1:34:23 PM 'SourceTimestamp: 11/28/2019 1:34:23 PM 'StatusCode: Good
The program output may look like this:
You can configure parameters of the Console Interaction by finding ConsoleInteractionParameters in the shared plug-ins configurations, and changing properties of the object obtained.
// This example shows how to completely turn off interaction in a console application. using System; using OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA; using OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.Engine; using OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.OperationModel; namespace UADocExamples.Interaction { partial class ConsoleInteraction { public static void TurnOff() { // Do not implicitly trust any endpoint URLs. EasyUAClient.SharedParameters.EngineParameters.CertificateAcceptancePolicy.TrustedEndpointUrlStrings.Clear(); // Completely disable the console interaction. EasyUAClient.SharedParameters.PluginSetups.FindName("UAConsoleInteraction").Enabled = false; // Define which server we will work with. UAEndpointDescriptor endpointDescriptor = "opc.tcp://opcua.demo-this.com:51210/UA/SampleServer"; // Require secure connection, in order to enforce the certificate check. endpointDescriptor.EndpointSelectionPolicy = UAMessageSecurityModes.Secure; // Instantiate the client object. var client = new EasyUAClient(); UAAttributeData attributeData; try { // Obtain attribute data. // The operation will fail, unless you set up mutual trust using certificate stores. attributeData = client.Read(endpointDescriptor, "nsu=http://test.org/UA/Data/ ;i=10853"); } catch (UAException uaException) { Console.WriteLine("*** Failure: {0}", uaException.GetBaseException().Message); return; } // Display results. Console.WriteLine("Value: {0}", attributeData.Value); Console.WriteLine("ServerTimestamp: {0}", attributeData.ServerTimestamp); Console.WriteLine("SourceTimestamp: {0}", attributeData.SourceTimestamp); Console.WriteLine("StatusCode: {0}", attributeData.StatusCode); } } }
# This example shows how to completely turn off interaction in a console application. # The QuickOPC package is needed. Install it using "pip install opclabs_quickopc". import opclabs_quickopc # Import .NET namespaces. from OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA import * from OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.Engine import * from OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.OperationModel import * # Do not implicitly trust any endpoint URLs. We want the user be asked explicitly. EasyUAClient.SharedParameters.EngineParameters.CertificateAcceptancePolicy.TrustedEndpointUrlStrings.Clear() # Completely disable the console interaction. EasyUAClient.SharedParameters.PluginSetups.FindName('UAConsoleInteraction').Enabled = False # Define which server we will work with. endpointDescriptor = UAEndpointDescriptor('opc.tcp://opcua.demo-this.com:51210/UA/SampleServer') # Require secure connection, in order to enforce the certificate check. endpointDescriptor.EndpointSelectionPolicy = UAEndpointSelectionPolicy(UAMessageSecurityModes.Secure) # Instantiate the client object. client = EasyUAClient() try: # Obtain attribute data. # The operation will fail, unless you set up mutual trust using certificate stores. attributeData = IEasyUAClientExtension.Read(client, endpointDescriptor, UANodeDescriptor('nsu=http://test.org/UA/Data/ ;i=10853')) except UAException as uaException: print('*** Failure: ' + uaException.GetBaseException().Message) exit() # Display results. print('Value: ', attributeData.Value) print('ServerTimestamp: ', attributeData.ServerTimestamp) print('SourceTimestamp: ', attributeData.SourceTimestamp) print('StatusCode: ', attributeData.StatusCode) print() print('Finished.')
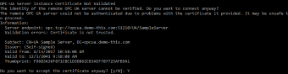
The example below configures the component to use uncolorized console output, and then triggers some user interaction.
// Shows how to configure the OPC UA Console Interaction plug-in by turning off the output colorization. using System; using System.Diagnostics; using OpcLabs.BaseLib.Console.Interaction; using OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA; using OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.Engine; using OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.OperationModel; namespace UADocExamples.Interaction { partial class ConsoleInteraction { public static void ColorizeOutput() { // Configure the shared plug-in. // Find the parameters object of the plug-in. ConsoleInteractionParameters consoleInteractionPluginParameters = EasyUAClient.SharedParameters.PluginConfigurations.Find<ConsoleInteractionParameters>(); Debug.Assert(consoleInteractionPluginParameters != null); // Change the parameter. consoleInteractionPluginParameters.ColorizeOutput = false; // Do not implicitly trust any endpoint URLs. We want the user be asked explicitly. EasyUAClient.SharedParameters.EngineParameters.CertificateAcceptancePolicy.TrustedEndpointUrlStrings.Clear(); // Define which server we will work with. UAEndpointDescriptor endpointDescriptor = "opc.tcp://opcua.demo-this.com:51210/UA/SampleServer"; // Require secure connection, in order to enforce the certificate check. endpointDescriptor.EndpointSelectionPolicy = new UAEndpointSelectionPolicy(UAMessageSecurityModes.Secure); // Instantiate the client object. var client = new EasyUAClient(); UAAttributeData attributeData; try { // Obtain attribute data. // The component automatically triggers the necessary user interaction during the first operation. attributeData = client.Read(endpointDescriptor, "nsu=http://test.org/UA/Data/ ;i=10853"); } catch (UAException uaException) { Console.WriteLine("*** Failure: {0}", uaException.GetBaseException().Message); return; } // Display results. Console.WriteLine("Value: {0}", attributeData.Value); Console.WriteLine("ServerTimestamp: {0}", attributeData.ServerTimestamp); Console.WriteLine("SourceTimestamp: {0}", attributeData.SourceTimestamp); Console.WriteLine("StatusCode: {0}", attributeData.StatusCode); } } }
# Shows how to configure the OPC UA Console Interaction plug-in by turning off the output colorization. # The QuickOPC package is needed. Install it using "pip install opclabs_quickopc". import opclabs_quickopc # Import .NET namespaces. from OpcLabs.BaseLib.Console.Interaction import * from OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA import * from OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.Engine import * from OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.OperationModel import * # Configure the shared plug-in. # Find the parameters object of the plug-in. consoleInteractionPluginParameters = EasyUAClient.SharedParameters.PluginConfigurations.Find[ConsoleInteractionParameters]() assert consoleInteractionPluginParameters is not None # Change the parameter. consoleInteractionPluginParameters.ColorizeOutput = False # Do not implicitly trust any endpoint URLs. We want the user be asked explicitly. EasyUAClient.SharedParameters.EngineParameters.CertificateAcceptancePolicy.TrustedEndpointUrlStrings.Clear() # Define which server we will work with. endpointDescriptor = UAEndpointDescriptor('opc.tcp://opcua.demo-this.com:51210/UA/SampleServer') # Require secure connection, in order to enforce the certificate check. endpointDescriptor.EndpointSelectionPolicy = UAEndpointSelectionPolicy(UAMessageSecurityModes.Secure) # Instantiate the client object. client = EasyUAClient() try: # Obtain attribute data. # The component automatically triggers the necessary user interaction during the first operation. attributeData = IEasyUAClientExtension.Read(client, endpointDescriptor, UANodeDescriptor('nsu=http://test.org/UA/Data/ ;i=10853')) except UAException as uaException: print('*** Failure: ' + uaException.GetBaseException().Message) exit() # Display results. print('Value: ', attributeData.Value) print('ServerTimestamp: ', attributeData.ServerTimestamp) print('SourceTimestamp: ', attributeData.SourceTimestamp) print('StatusCode: ', attributeData.StatusCode) print() print('Finished.')
' Shows how to configure the OPC UA Console Interaction plug-in by turning off the output colorization. Imports OpcLabs.BaseLib.Console.Interaction Imports OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA Imports OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.Engine Imports OpcLabs.EasyOpc.UA.OperationModel Namespace Interaction Friend Class ConsoleInteraction Public Shared Sub ColorizeOutput() ' Configure the shared plug-in. ' Find the parameters object of the plug-in. Dim consoleInteractionPluginParameters = EasyUAClient.SharedParameters.PluginConfigurations.Find(Of ConsoleInteractionParameters)() Debug.Assert(consoleInteractionPluginParameters IsNot Nothing) ' Change the parameter. consoleInteractionPluginParameters.ColorizeOutput = False ' Do not implicitly trust any endpoint URLs. We want the user be asked explicitly. EasyUAClient.SharedParameters.EngineParameters.CertificateAcceptancePolicy.TrustedEndpointUrlStrings.Clear() ' Define which server we will work with. Dim endpointDescriptor As UAEndpointDescriptor = "opc.tcp://opcua.demo-this.com:51210/UA/SampleServer" ' Require secure connection, in order to enforce the certificate check. endpointDescriptor.EndpointSelectionPolicy = New UAEndpointSelectionPolicy(UAMessageSecurityModes.Secure) ' Instantiate the client object. Dim client = New EasyUAClient() Dim attributeData As UAAttributeData Try ' Obtain attribute data. ' The component automatically triggers the necessary user interaction during the first operation. attributeData = client.Read(endpointDescriptor, "nsu=http://test.org/UA/Data/ ;i=10853") Catch uaException As UAException Console.WriteLine("*** Failure: {0}", uaException.GetBaseException.Message) Exit Sub End Try ' Display results. Console.WriteLine("Value: {0}", attributeData.Value) Console.WriteLine("ServerTimestamp: {0}", attributeData.ServerTimestamp) Console.WriteLine("SourceTimestamp: {0}", attributeData.SourceTimestamp) Console.WriteLine("StatusCode: {0}", attributeData.StatusCode) End Sub End Class End Namespace
// Shows how to configure the OPC UA Console Interaction plug-in by turning off the output colorization. class procedure ConsoleInteraction.ColorizeOutput; var Arguments: OleVariant; AttributeData: _UAAttributeData; Client: OpcLabs_EasyOpcUA_TLB._EasyUAClient; ClientManagement: TEasyUAClientManagement; ConsoleInteractionParameters: _ConsoleInteractionParameters; EndpointSelectionPolicy: _UAEndpointSelectionPolicy; ReadArguments: _UAReadArguments; Result: _UAAttributeDataResult; Results: OleVariant; begin // Configure the shared plug-in. // The configuration object allows access to static behavior. ClientManagement := TEasyUAClientManagement.Create(nil); ClientManagement.Connect; // Find the parameters object of the plug-in. ConsoleInteractionParameters := IUnknown(ClientManagement.SharedParameters.PluginConfigurations.Find('OpcLabs.BaseLib.Console.Interaction.ConsoleInteractionParameters')) as _ConsoleInteractionParameters; // Change the parameter. ConsoleInteractionParameters.ColorizeOutput := False; // Do not implicitly trust any endpoint URLs. We want the user be asked explicitly. ClientManagement.SharedParameters.EngineParameters.CertificateAcceptancePolicy.TrustedEndpointUrlStrings.Clear(); // Define which server we will work with. ReadArguments := CoUAReadArguments.Create; ReadArguments.EndpointDescriptor.UrlString := 'opc.tcp://opcua.demo-this.com:51210/UA/SampleServer'; // Require secure connection, in order to enforce the certificate check. EndpointSelectionPolicy := CoUAEndpointSelectionPolicy.Create; EndpointSelectionPolicy.AllowedMessageSecurityModes := UAMessageSecurityModes_Secure; ReadArguments.EndpointDescriptor.EndpointSelectionPolicy := EndpointSelectionPolicy; ReadArguments.NodeDescriptor.NodeId.ExpandedText := 'nsu=http://test.org/UA/Data/ ;i=10853'; Arguments := VarArrayCreate([0, 0], varVariant); Arguments[0] := ReadArguments; // Instantiate the client object. Client := CoEasyUAClient.Create; // Obtain attribute data. // The component automatically triggers the necessary user interaction during the first operation. TVarData(Results).VType := varArray or varVariant; TVarData(Results).VArray := PVarArray(Client.ReadMultiple(Arguments)); Result := IInterface(Results[0]) as _UAAttributeDataResult; if Result.Succeeded then begin AttributeData := Result.AttributeData; // Display results. WriteLn('Value: ', AttributeData.Value); WriteLn('ServerTimestamp: ', DateTimeToStr(AttributeData.ServerTimestamp)); WriteLn('SourceTimestamp: ', DateTimeToStr(AttributeData.SourceTimestamp)); WriteLn('StatusCode: ', AttributeData.StatusCode.ToString); end else WriteLn('*** Failure: ', Result.ErrorMessageBrief); VarClear(Results); VarClear(Arguments); FreeAndNil(ClientManagement); end;
The program output may look like this:
Copyright © 2004-2023 CODE Consulting and Development, s.r.o., Plzen. All rights reserved. Web page: www.opclabs.com
Send Documentation Feedback. Resources: Knowledge Base. Technical support: Online Forums, FAQ.